n8n
Self-hostable workflow automation platform with 400+ integrations, visual flows, webhooks, and custom code for building reliable integrations and internal automations.
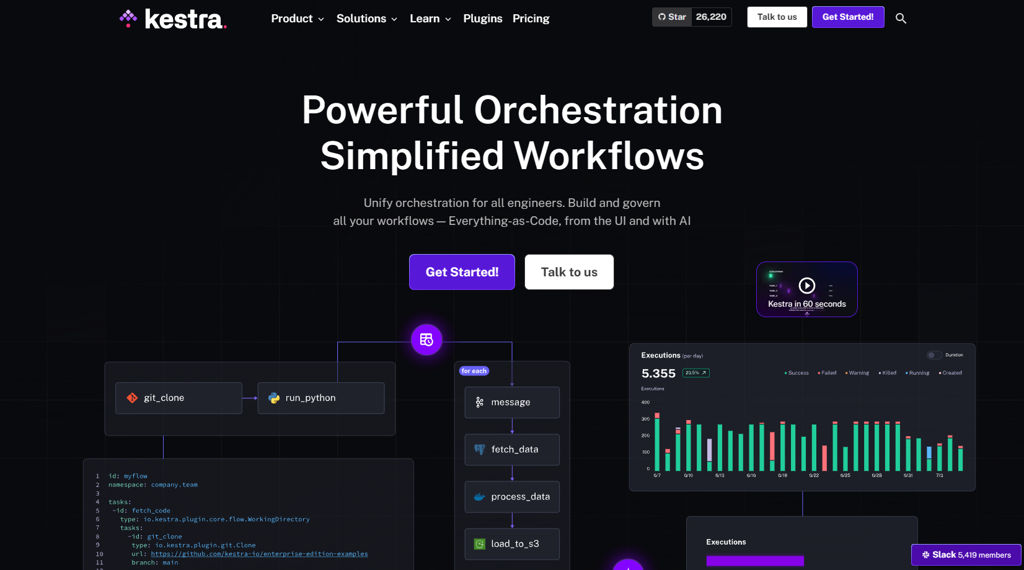
n8n is a workflow automation platform for building integrations and automations across apps, APIs, and internal systems. It provides a visual editor for creating multi-step workflows, with the option to add custom code and handle complex data transformations.
Key Features
- Visual workflow editor with triggers, branching/IF logic, loops, and data mapping
- Large library of prebuilt integration nodes (HTTP/API, SaaS apps, databases) plus generic HTTP Request node
- Webhooks for event-driven automation and building lightweight API endpoints
- Code and scripting steps (e.g., JavaScript) for custom logic and transformations
- Credentials management for connecting services securely
- Scheduling and polling triggers for time-based or interval automations
- Execution history and tooling to debug runs and inspect data
- Queue/worker execution mode for scaling and isolating job processing
Use Cases
- Sync data between CRM, spreadsheets, and databases with transformations
- Automate support/ops workflows (ticket enrichment, notifications, escalations)
- Build internal integrations using webhooks + custom logic without a full app
Limitations and Considerations
- Some advanced capabilities (e.g., certain governance/enterprise controls) may depend on paid offerings
- Complex workflows can require careful error handling/retries design to be resilient at scale
n8n fits teams that want an approachable low-code automation tool while keeping the option to write code for edge cases. It is commonly used to replace ad-hoc scripts and brittle point-to-point integrations with observable, reusable workflows.